컴퓨터구조
0. Intro > 0-2. CA Overview
CA Overview
Updated at 2022.09.11
Below your program
A simplified view of hardware and software
- Applications software
- Written in high-level language
- Systems software
- Compilers: translate high-level language to machine language
- Operating Systems
- Handle input/output operations
- Manage resources (e.g., storage, memory)
- Schedule tasks (processes)
- Hardware
- processors memory, I/O devices
Execution of programs
Step 1: Translating language
- From high-level language
- Designed for specific domain
- Provides for productivity and portability
- To hardware machine language
- Binary digits
- Encoded instructions
Step 2: Inputting, outputting, processing, and storing data
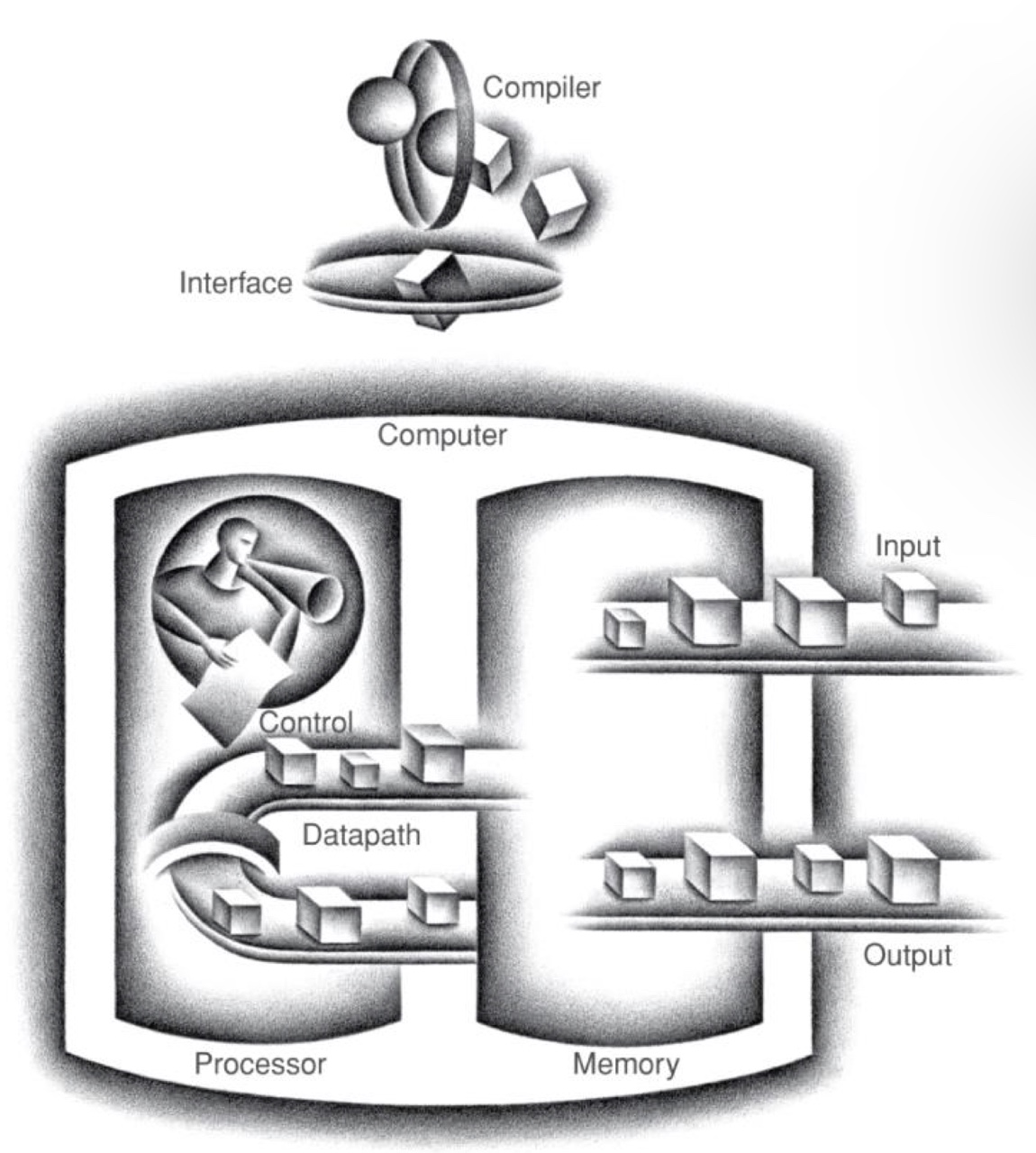
4 Fundamental HW components
- Processor
- Datapath + control, our primary focus
- Memory
- Input device
- Keyboard, mouse, ...
- Output device
- Screen, speaker
8 STEPS
- Loading: programs are stored in memory
- Inputting: input device write data to memory
- Fetching: processor fetches instructions and data from memory
- Decoding: processor (control) decodes the instructions and determine what to do
- Executing : processor (datapath) executes the instructions & stores the computation result to memory
- Outputting: output device sends the result by reading output data from memory
Understanding program performance
- Algorithm
- Determines the number of operations executed
- Programming language, compiler, and instruction set architecture (ISA)
- Determine the number of machine instructions executed per operation
- Processor and memory system
- Determine how fast instructions can be executed
- I/O system (including OS)
- Determines how fast I/O operations are executed
What is ISA (Instruction Set Architecture)
- An interface between SW snd HW (includes a set of machine instruction)
- SW is translated into the machine instructions included in the ISA
- HW is designed to support the instructions in ISA
8 great ideas for designing better computer architecture
- Design for Moore's Law
- Anticipate where the technology will be when the design finishes
- Provide abstraction to simplify design
- Hide low-level details for the ease of SW development
- Make the common case fast
- Enhance performance of the common case instead of optimizing the rare case.
- Perform via parallelism
- Perform operations in parallel
- Performance via pipelining
- Use a particular patten of parallelism, called pipelining
- Performance via prediction
- Start working with prediction, stead of waiting until you know for sure
- Hierarchy of memories
- Use the fastest, smallest, and most expensive memory at the top of the hierarchy and the slowest, largest, and cheapest memory at the bottom
- cache > RAM > Large SSD
- Dependability via redundancy
- Include redundant components that can take over when failure occurs