컴퓨터구조
3. Arithmetic for Computers > 3-3. Division
Division
Updated at 2022.10.06
Division
If the length of Dividend and Divisor is M and N,
the length of Quotient M - N + 1 & the length of Remainder N
- In MIPS-based computers, 32 bits are used to represent both Dividend and Divisor.
Therefore, the length of both Quotient and Remainder 32
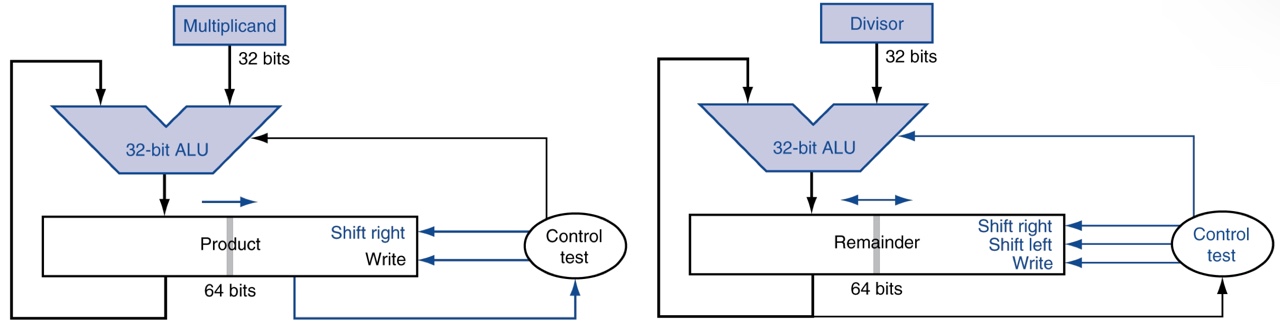
Optimized version of the division HW
- 32-bit divisor register / ALU
- 64-bit remainder register (dividend and quotient shares a register with remainder)
HI: RemainderLO: Quotient
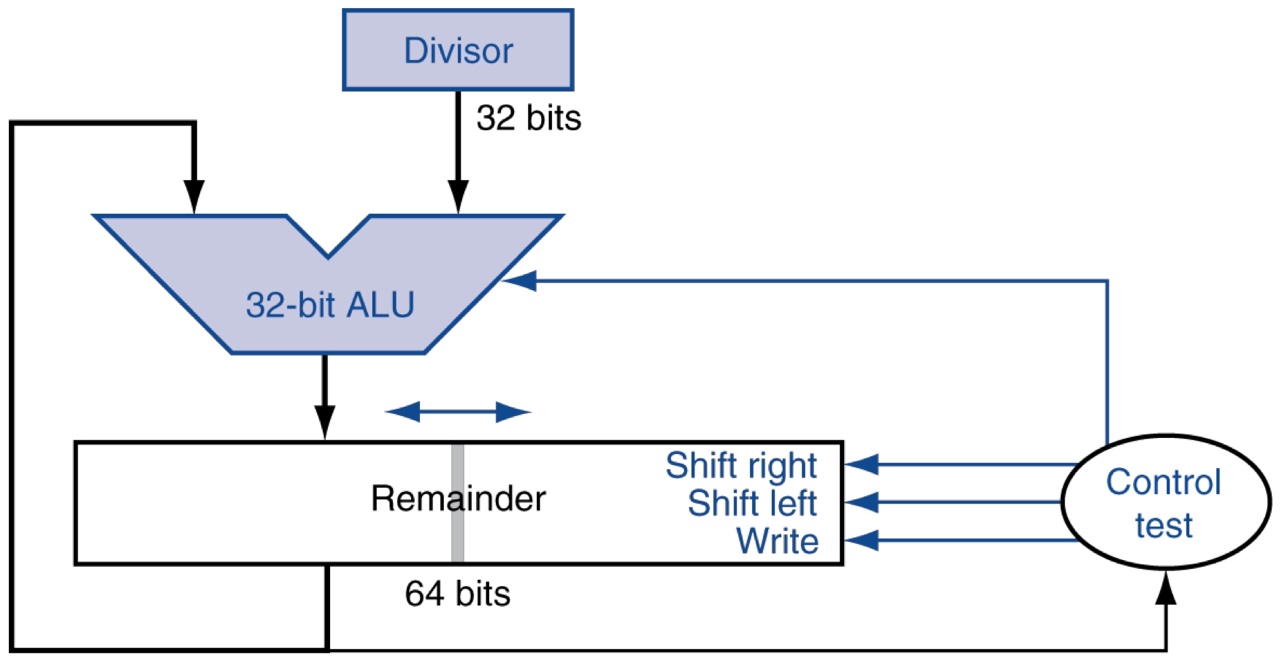
Settings
- 0 is stored in the left half of the Remainder register
- The value of dividend is loaded into the right half of the Remainder register
- The value of divisor is loaded into the Divisor register
Division Algorithm
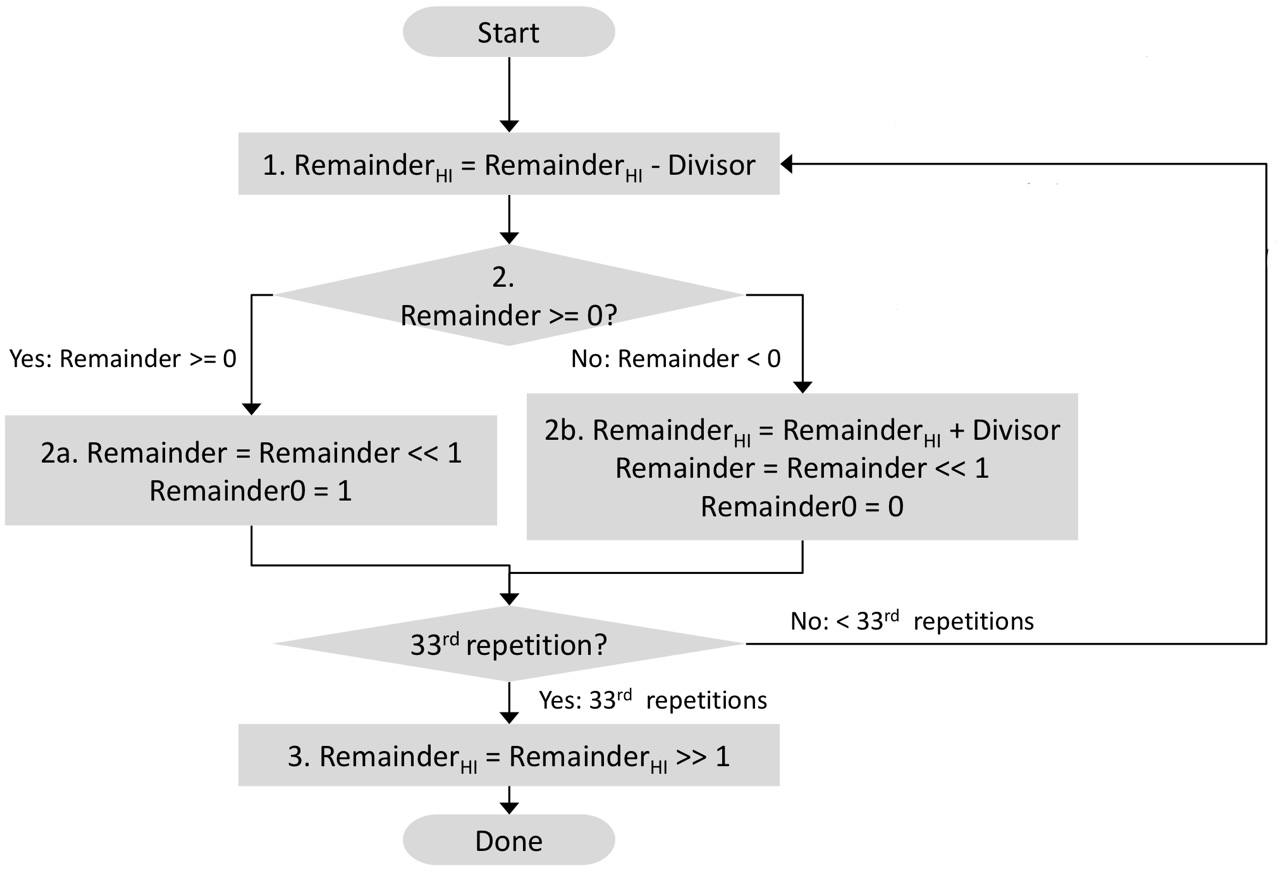
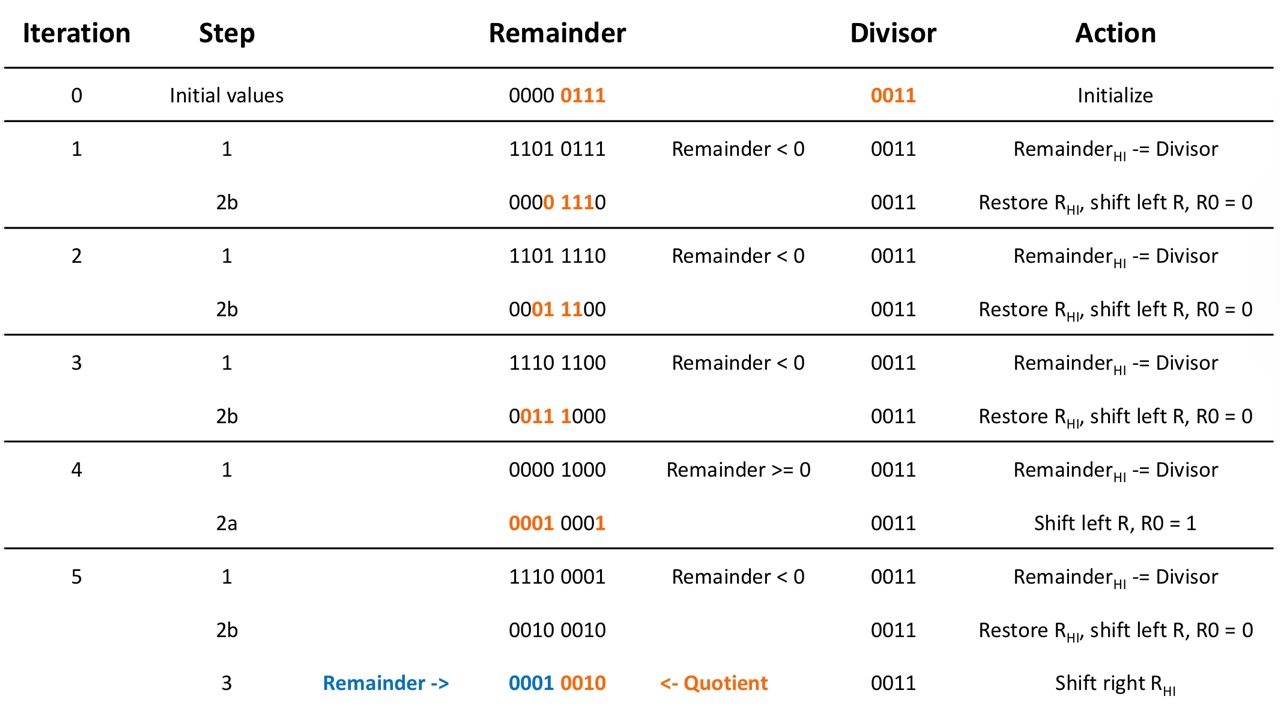
Example
When N = 4 (4-bit ALU / divisor, 8-bit product),
- should be repeated as many bits + 1 as it is
Signed division
Do division after converting both divisor & dividend to positives
After the division
- Negate the quotient only if the signs of the divisor and dividend are different
- Remainder's sign follows Dividend's sign
Instructions
div rs, rt / divu rs, rt: do$rs/$st- The result (remainder and quotient) is stored in
HI/LO - No overflow or divide-by-0 checking
- The result (remainder and quotient) is stored in

Example:
- Initially, the value in
$t0(dividend) is loaded into theLOregister - Initially,
$t(divisor) is used as the divisor register - Then, do the division and store the remainder and quotient to
HIandLOregisters
Summary: Design for arithmetic operations
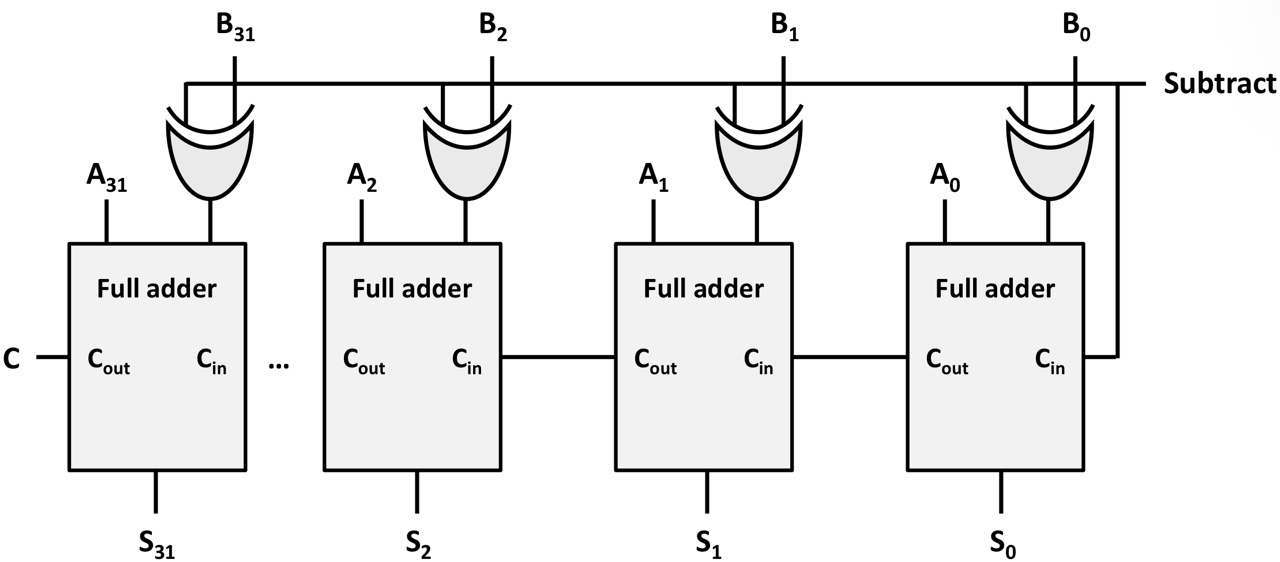
Addition & Subtraction
Use the same HW for addition and subtraction
- 32-bit parallel adder
- Additional XOR operators + subtract bit
Multiplication & Division
Use the same optimized HW for Multiplication and Division
- A single 32-bit register for multiplicand and divisor
- A single 32-bit
ALU HIandLOregisters for the results of multiplication and division