컴퓨터구조
1. Computer Abstractions and Technology > 1-1. Defining Performance
Defining Performance
Updated at 2022.09.12
Two metrics for defining computer performances
- Response time
- The time between the start and completion of a task
- related to single task
- e.g., how long it takes to do a single task
- Throughput
- A total amount of works done per unit time
- related to multiple tasks
- e.g., tasks per hour
Q. If we replace the processor in a computer with ad faster version
- Response time decrease
- Throughput increase
Q. If we add more processors to a system
- Response time maintain or increase (more lanes more complex)
- Throughput increase
Defining performance
- Relative performance: X is N time faster than Y
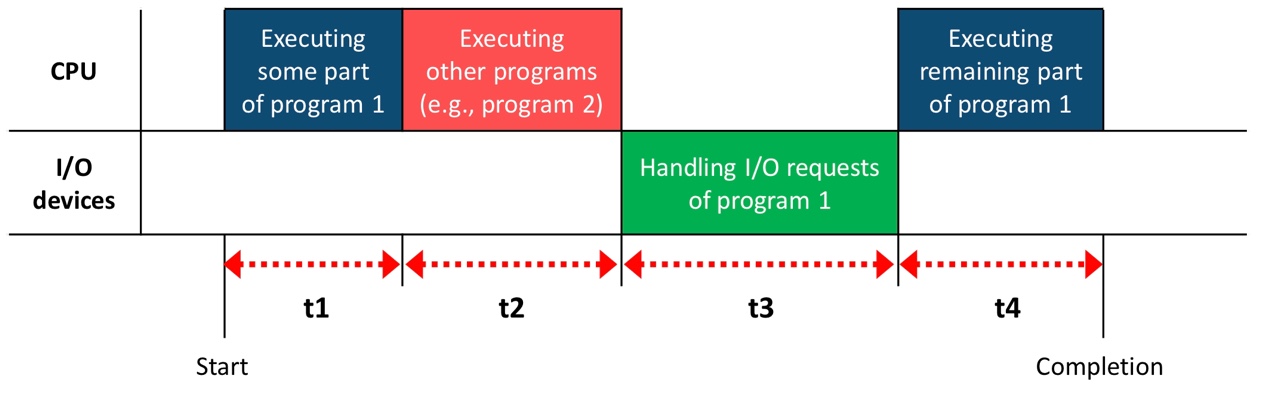
- Elapsed time = system performance = t1 + t2 + t3 + t4
- total time between the start and completion of a task, including everything
- CPU time = CPU performance = t1 + t4 (Only this in this class)
- The time spent processing a given task on a processor
The CPU time can be further divided into
- User CPU time
- spent for processing the code of the program (some functions)
- System CPU time
- spent in the operating system performing tasks for the program (OS)