컴퓨터구조
4. The Processor > 4-3. A single-cycle datapath
A single-cycle datapath
Updated at 2022.10.14
Single-cyle datapath
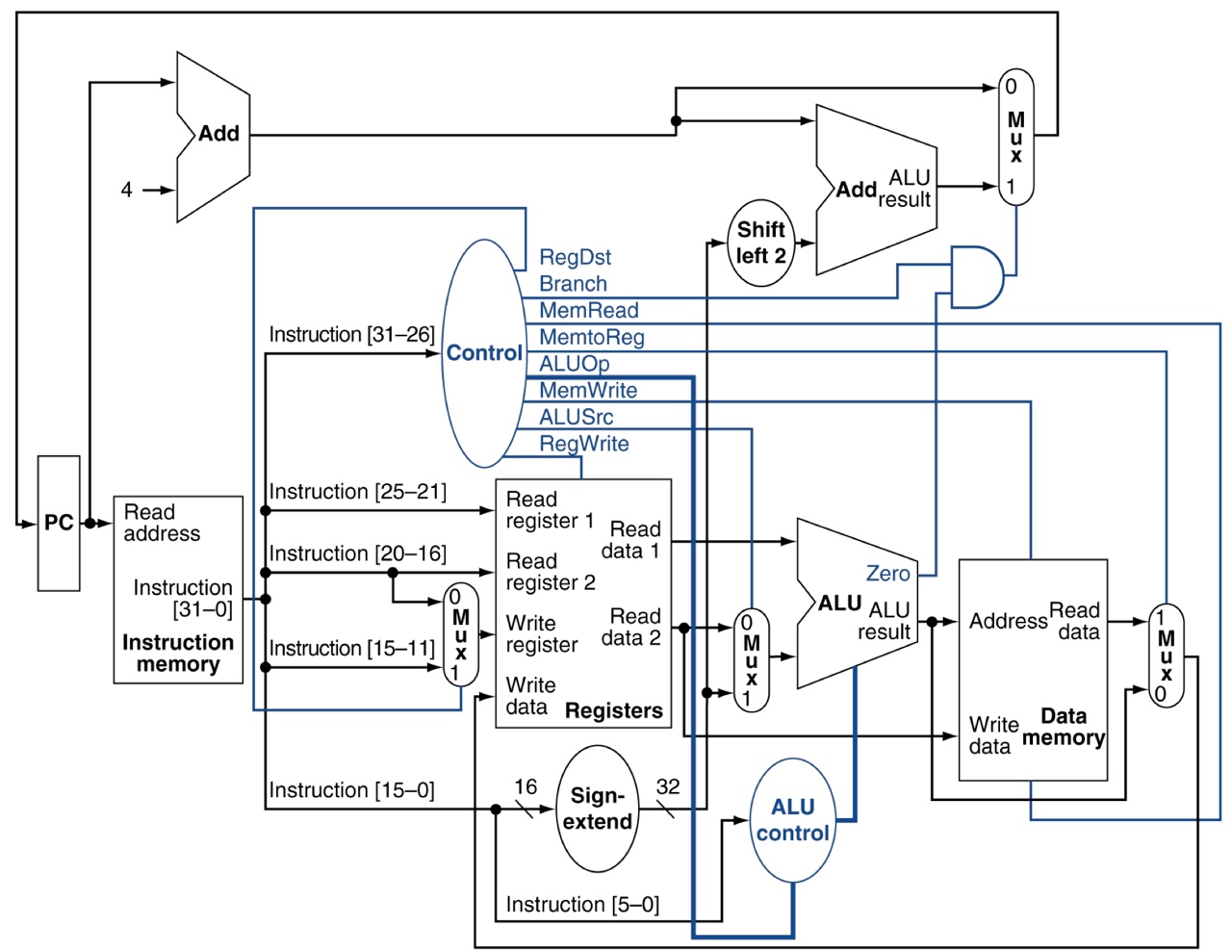 Whole structure of Processor
Whole structure of Processor
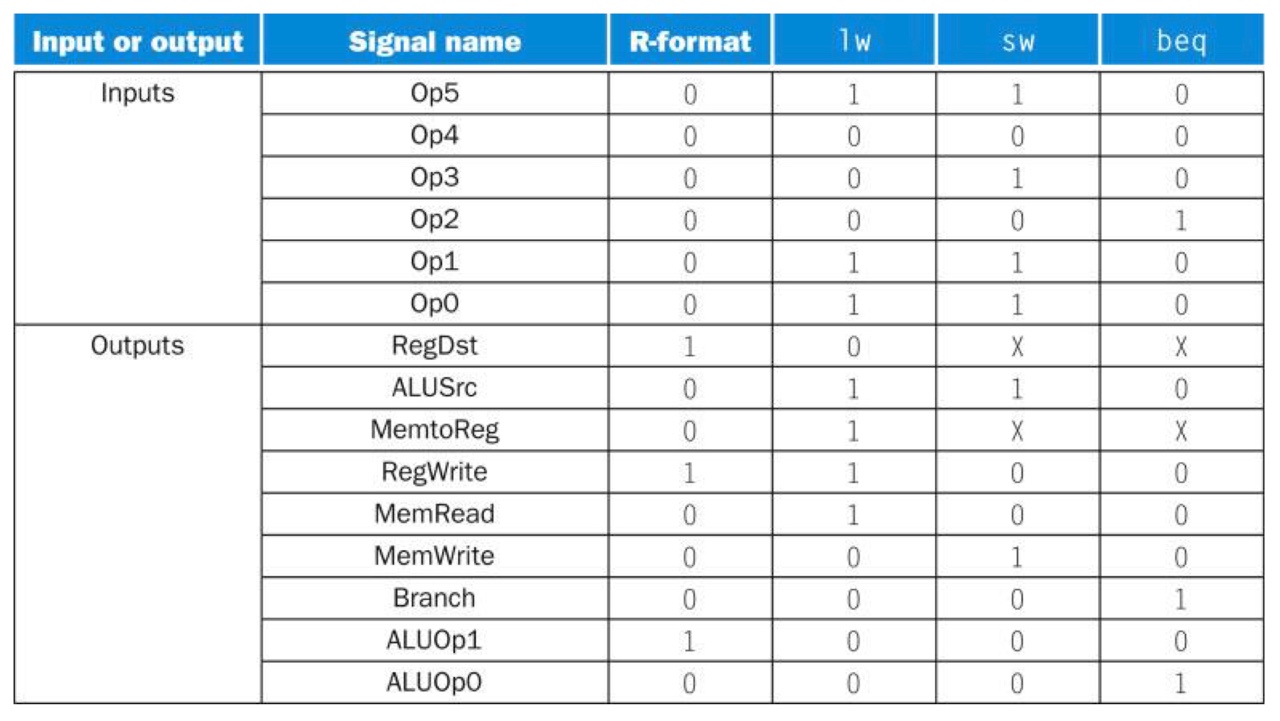 Signal with controller
Signal with controller
A single-cycle datapath executes instructions in one clock cycle with a clocking methodology.
We will study how this works according to instructions
R-format
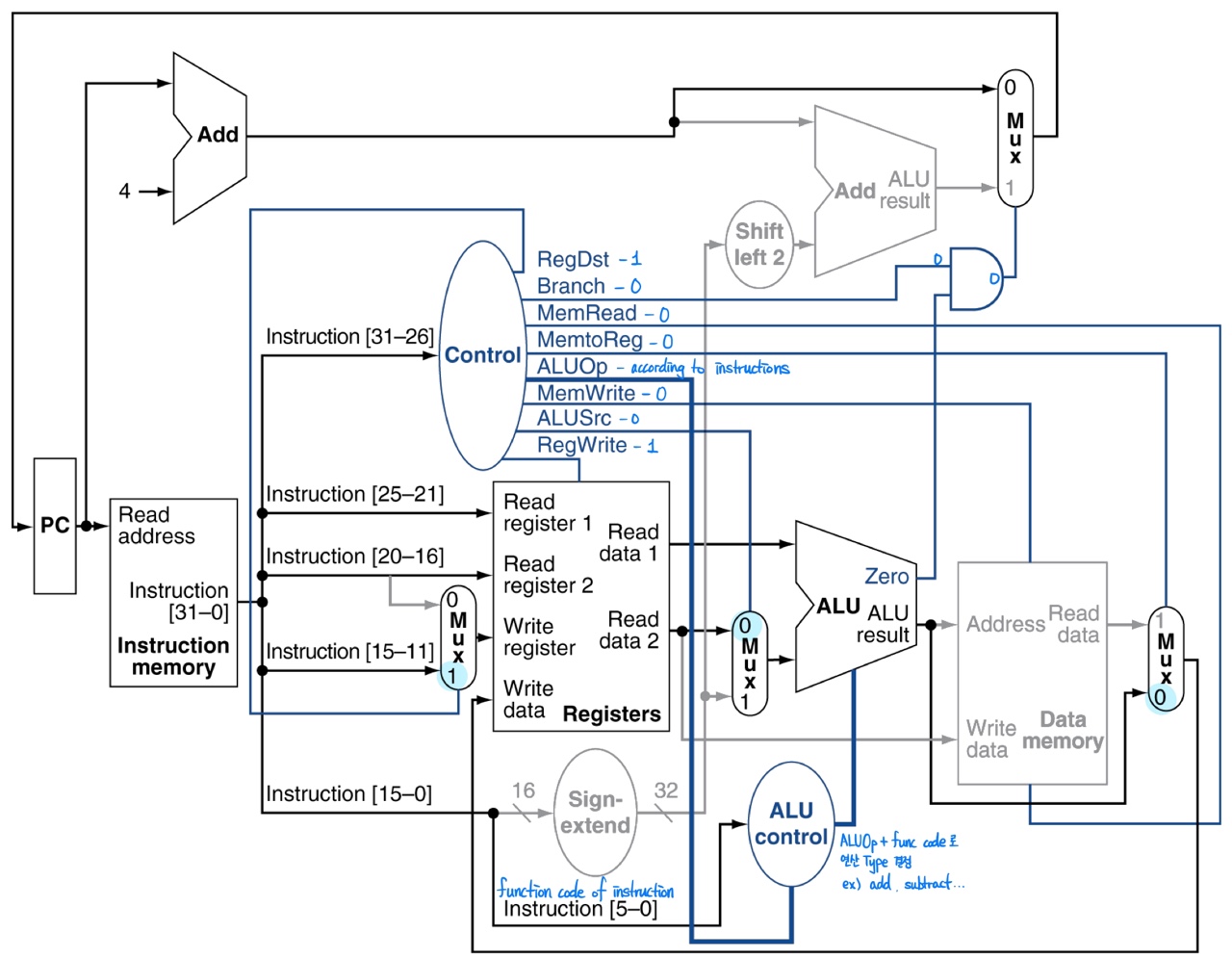 R-format
R-format
- don't need to access memory
MemRead= 0MemtoReg= 0MemWrite= 0
- have to update value of
rdregisterRegDst= 1RegWrite= 1
- PC just have to be updated +4
branch= 0
- ALU control determines the arithmetic type according to
ALUOpandfunc codeof instruction
Load
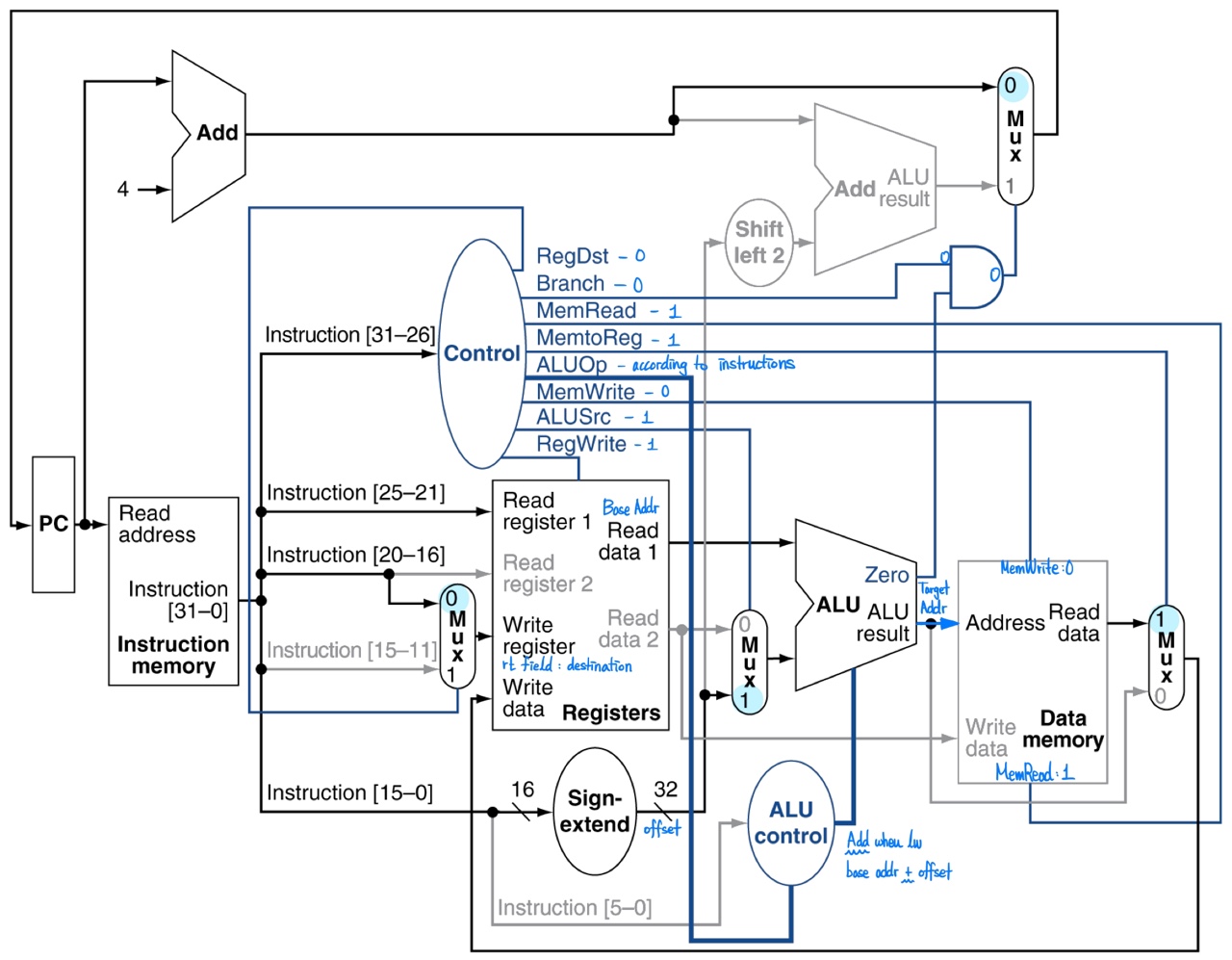 Load
Load
- need to access memory and read data
MemRead= 1MemtoReg= 1MemWrite= 0
- have to get value from memory to
rsfield (destination)RegDst= 0 (rsto destination)RegWrite= 1
- PC just have to be updated +4
branch= 0
- ALU control determines the arithmetic type according to
ALUOp - offset is extended from 16-bit to 32-bit by Sign-extend unit and added with Read data 1 (base addr)
Branch-on-equal
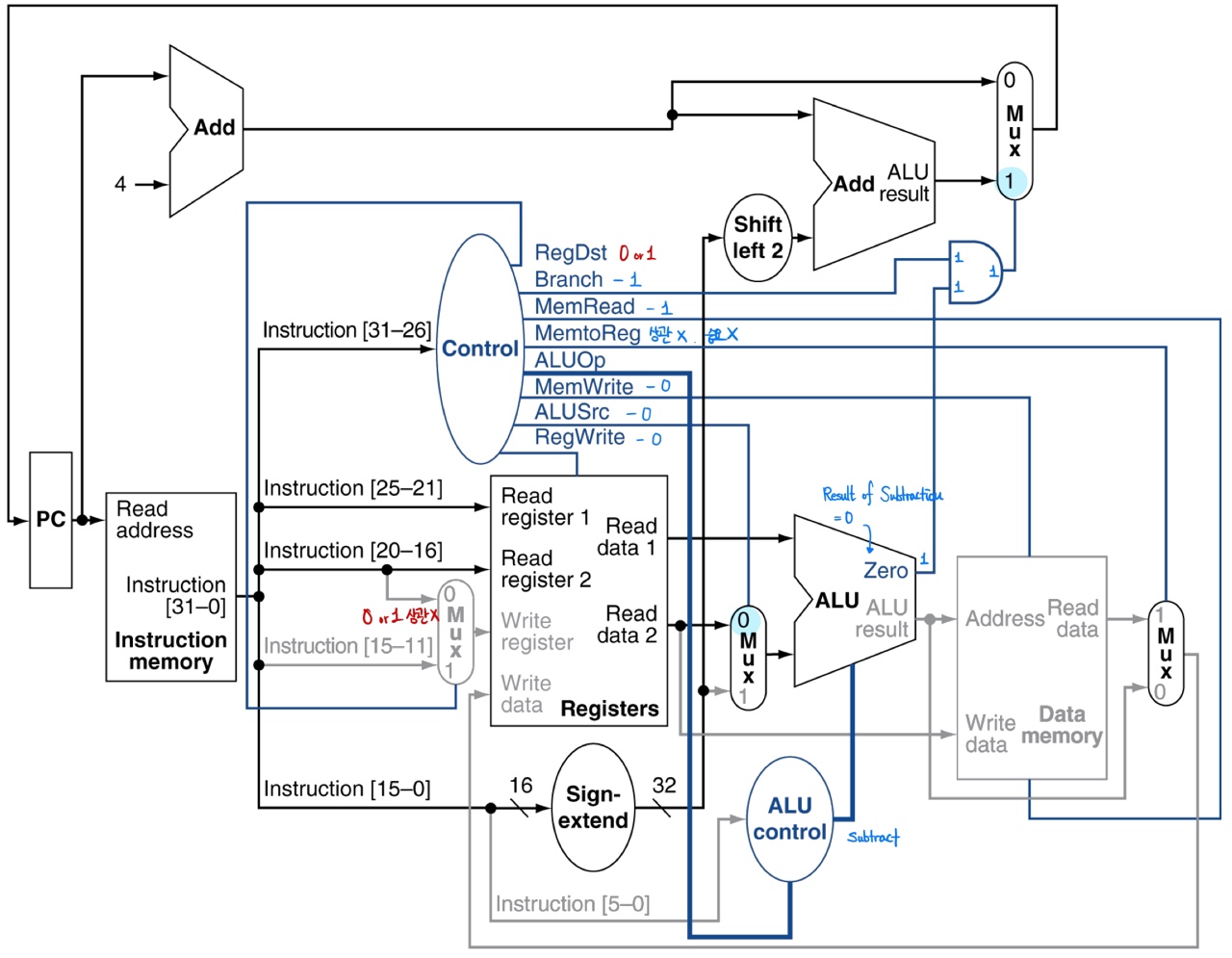 Branch-on-equal
Branch-on-equal
- don't need to access memory
MemRead= 0MemtoReg= 0MemWrite= 0
- Calculate target address
- extend the offset to 32 bit and shift left twice (multiply 4)
- add with
PC + 4
RegDstdoesn't matter
More about: jump
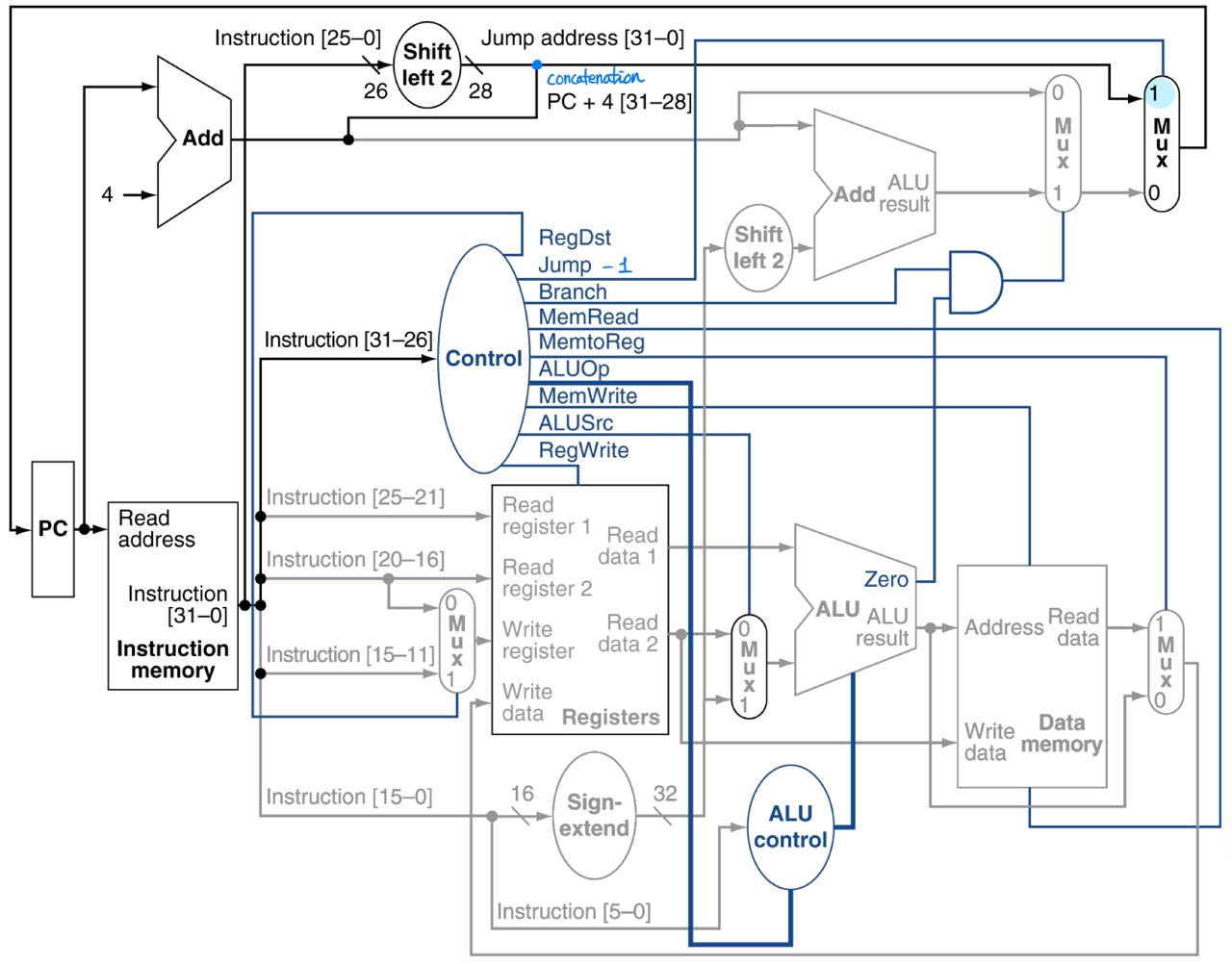 Jump
Jump
- Calculate target address
- offset is extended to 28-bit
- concatenate with
0000
Jump signal = 1